EDI (ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE)
ELECTRONIC DATA INTERCHANGE

Components
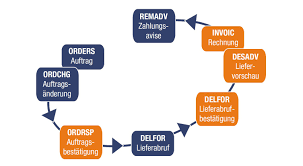
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) in logistics refers to the electronic exchange of business documents between trading partners in the logistics industry. EDI is a standardized method of exchanging information between computer systems, allowing for seamless and efficient communication between different parties in the supply chain.
In the logistics industry, EDI is commonly used to exchange information related to orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other documents between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. The use of EDI can help improve supply chain efficiency, reduce errors, and minimize the time and cost associated with manual data entry and processing.
BENEFITS OF EDI
1. Improved accuracy and speed: EDI allows for the automatic transfer of data between computer systems, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors. This can help speed up order processing and improve the accuracy of information exchanged between trading partners.
2. Enhanced visibility and tracking: EDI can provide real-time visibility into the status of orders and shipments, allowing for better tracking and management of inventory and logistics operations.
3. Cost savings: By reducing the need for paper-based processes and manual data entry, EDI can help businesses save time and money on administrative tasks.
4. Improved customer service: By providing real-time updates on the status of orders and shipments, EDI can help improve customer satisfaction and reduce customer inquiries.
EDI
To implement EDI in logistics, businesses typically use specialized software systems that are capable of transmitting and receiving electronic messages in the standardized EDI format. These systems can be integrated with other logistics software, such as transportation management systems (TMS) or warehouse management systems (WMS), to streamline operations and improve supply chain visibility.
